LVM Carries out Forestry Measures to Protect Young Stands
Autumn and winter are the time when cervids have limited access to nutrients, lacking shoots, leaves and grass of dwarf shrubs in the forest, which results in the animals looking for conifers to take in the necessary nutrients directly from the needles and tree bark. Forestry, on the other hand, aims to produce productive, valuable and healthy forest stands. Currently, this objective is hampered by the increasing numbers of forest animals and the damage they cause to restored forest areas.
Hunting is the most effective way to regulate the numbers of animals, taking into account the interests of both hunters and foresters. Successful reduction of game animal damage requires good cooperation between landowners and tenants of hunting rights. The first step in providing this, is the exchange of information on the damage caused by game animals and the areas where forest protection work has been carried out, because hunters need to know where more intensive hunting should be organized. Today, when it is allowed to organize hunting with hunting dogs, it is important to organize it on a regular basis in order to minimize the risk of animals staying in one particular area, thus creating a greater chance of causing damage to restored forest areas.
Forest owners and managers can also limit damage by implementing restored area conservation measures and forestry activities that, in the long run, can provide additional food for forest animals and protect target trees from damage.
JSC “Latvia’s State Forests” (LVM) has implemented a number of measures in its economic activities to create an additional food base for forest animals and the company monitors their efficiency on a regular basis.
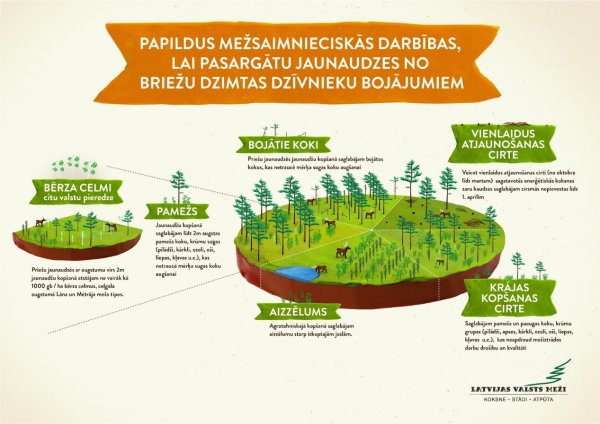
When carrying out young stand tending, undergrowth of tree and shrub species (rowan, willow, oak, ash, linden, maple, etc.) at the height of up to 2 metres that do not interfere with the growth of the target species are preserved. These species of undergrowth trees and shrubs are often damaged, thus driving out new shoots that are damaged repeatedly.
When performing young pine stand tending, any damaged trees that do not interfere with the growth of the target species are preserved. These damaged trees tend to be damaged repeatedly by forest animals, thus reducing the risk of damage to other healthy trees growing in the forest.
When performing thinning, groups or bands of undergrowth trees and shrubs (rowan, ash, aspen, willow, oak, ash, linden, maple, etc.) that do not compromise the safety and quality of logging works are preserved. Such groups or bands of trees and shrubs serve both as a supplementary food base and as a refuge for animals.
In case of seamless renewal felling from October to March, it is valuable to keep the prepared pile of energy wood branches untreated until the spring. It is often observed that game animals feed on branches of timber stacked in piles, especially aspen and pine.
Through cooperation of skilled foresters and hunters, balance between forestry and hunting can be reached.